Analysis Of Factors Affecting Mobile Commerce in India
2025, Vol.02, Issue 01 Pages 100-108
Ranju, and Bhushan, Bharat👤 ✉ ORCID: | DOI: https://doi.org/10.70388/sm240122
+ Add to Mendeley | 🔗 Share | View PDF
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
Citation
Ranju, & Bhushan, B. (2025). Analysis Of Factors Affecting Mobile Commerce in India. Shodh Manjusha: An International Multidisciplinary Journal, 02(01), 100–108. https://doi.org/10.70388/sm240122
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
ABSTRACT
India looks to be driving the shift from e-commerce to mobile commerce adoption. Apps and mobile websites are available in a wide range of sectors, including health, travel, commerce, ticketing, and leisure, offering considerable opportunities for both consumers and businesses. This study investigates and analyses the key factors that influence m-commerce transaction decisions. A single paradigm is utilized to investigate the significant moderating effect of demographics and mobile commerce service categories, such as banking, ticket booking, and shopping, on users’ behavioural intentions. M-Commerce and E-Commerce allowed people to transfer payments, shop, and bid without needing to visit stores in real time. E-commerce takes place on laptops and desktop computers connected to the internet, whereas M-Commerce takes place on mobile phones. M-Commerce refers to e-commerce via mobile phones. E-commerce pioneered anytime online transactions, whereas M-Commerce pioneered Anytime Anywhere online transactions. M-Commerce’s ubiquity, reachability, mobility, and flexibility have resulted in an increase in mobile users and mobile internet subscribers across India. Keywords: Crime, investigation, bail, imprisonment, juvenile, warrant, custody, legal assistance, offence.
By 2020, India is expected to become the second largest smartphone market after China, surpassing the US. This study focuses on M-Commerce, including its benefits and drawbacks, as well as its potential future expansion in India. M-Commerce has disadvantages such as a small device screen, slow CPUs, limited memory, poor resolutions, cumbersome data entering, a scarcity of WAP-enabled devices, high transmission speeds, and a shortage of bandwidth. According to the research, major elements influencing M-commerce adoption include trust, perceived privacy, perceived utility, subjective norms, perceived value contributed, perceived security, and perceived simplicity of use. All seven variables were statistically significant. Trust is seen to be the foundation for influencing the adoption behaviour of mobile users. This study’s conclusions benefit the telecom sector and online players.
Keywords: E- commerce, M- commerce, Internet, Smart Phone, Technology
1. INTRODUCTION
M-commerce is wireless electronic commerce carried out for business reasons via hand-held devices such as smartphones, tablets, and PDAs. Mobile devices are considered as personal journals, which drives up the number of mobile users. M-commerce is implemented using mobile applications. People utilize mobile applications rather than web applications to pay utility bills, purchase tickets, transfer funds, send emails, and so on. Thus, M-Commerce is replacing E-Commerce. Despite these advantages, M-Commerce has some disadvantages, including a small device screen, slow CPUs, limited memory, poor resolutions, cumbersome data entry, a shortage of WAP-enabled devices, high transmission speeds, and a lack of bandwidth. With nearly 83% of Indians owning a smartphone and shopping online via their phones, India’s m-commerce industry is predicted to expand. While many customers have used their mobile devices to shop online, there is still a lot of space for growth in terms of the frequency of online purchases. The fast growth of mobile devices and wireless networks has transformed E-commerce. The new E-commerce version, known as M-commerce, is gaining popularity among customers. M-commerce is a subgenre of e-commerce. E-commerce implementation began with the advent of the internet, but M-commerce adoption increased with the introduction of smart devices and wireless networks. M-commerce is a volatile and uncertain industry driven by technological improvements and consumer demand. Mobile commerce has various advantages over traditional electronic commerce, including ease of use, usefulness, reduced risk, and convenience. With the growth of the smartphone industry in India, M-commerce has emerged as the most promising business model. It has been observed that the intrinsic qualities of mobile technology, such as personalization, flexibility, and mobility, provide increased possibility for organizations to effectively capitalize on growing market opportunities. It is crucial, however, to look into the elements that drive m-commerce adoption in underdeveloped countries. Finally, the study will help m-commerce service providers understand the essential characteristics that drive m-commerce adoption.
Objectives
- To examine the factors affecting usage of M-commerce in India.
- Investigating the impact of mindset on the adoption of M-commerce.
Literature Review
- Zeinab Zamani, Hamid Padasn(2024): A research paper on predicting mobile commerce adoption: The SEM-MLP approach. This paper highlights the factors that impact the adoption of mobile commerce by consumer. Researcher reveals that compatibility, perceived usefulness, perceived risk, mobility and perceived cost have highly effect on the adoption of mobile commerce by consumers. But mobility and model variables had the greatest impact on the usage of mobile commerce. Perceived cost had the lowest effect on the usage of m-commerce.
- Swati Chauhan, Jaydev Bhatwadekar(2024): A research paper on digital formation in financial services: Assessing financial and digital literacy in eastern Madhya Pradesh. Objective of this study is to know about the status FL and DFS for informed policy decision. Secondly to access the FL and DFS awareness amongst different individuals. Researcher used primary data for this study. Researcher finds that positive corelation coefficient between FL and DFS awareness suggest a symbotic relationship. Average digital literacy in the region is more than average financial literacy. Researcher reveals that strong disparities are caused on the basis of social class, gender, education, occupation, income in the eastern Madhya Pradesh.
- Eslam Elgammal, Chat Chingtan(2023): A research paper on employing S-O-R approach in linking mobile commerce ubiquity with usage behaviour. Objective of this paper is to highlight the effect of mobile commerce on consumer behaviour. Ubiquity is a factor which effect brand trust and usage behaviour. Researcher finds that ubiquity positively impacted brand trust and positively influenced mobile commerce usage behaviour.
- M. Narayan(2023): Conducted a research paper on mobile commerce application an services: A study on customer perception. Objective of this study is to study the level of awareness of mobile commerce among customers and to analyse the usage of mobile commerce service and its applications. Researcher collect primary data from 100 respondents for this study through questionnaire. Researcher reveals that India is showing the positive prints of adoption of m-commerce platforms. Increasing demand of m-commerce application shows that it has penetrated the Indian market but till m-commerce at growing stage in India.
Advantages of Mobile Commerce
- Convenience: Customers can shop from anywhere at any time, making it convenient for them to make purchases on the go.
- Personalized experience: M-commerce allows for tailored marketing messages and personalized recommendations based on user behaviour and preferences.
- Speed: Mobile transactions can be completed quickly, reducing the time it takes for customers to make purchases.
- Accessibility: M-commerce reaches a wider audience as it can be accessed by anyone with a smartphone or tablet, making it easier for businesses to connect with customers.
- Cost-effective: M-commerce eliminates the need for maintaining physical stores, reducing overhead costs for businesses.
- Integration with social media: M-commerce can be integrated with social media platforms, allowing businesses to leverage their social media presence for sales and promotions.
- Location-based marketing: M-commerce can utilize location-based services to target customers based on their current location, allowing for more targeted and relevant marketing messages.
- Enhanced customer engagement: M-commerce apps can provide interactive features such as push notifications, customer reviews, and real-time customer support, increasing customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Analytics: Businesses can gather valuable data and insights from m commerce transactions, allowing them to understand customer purchasing behaviour and make informed business decisions.
- Scalability: M-commerce can easily scale to accommodate growth in customer base and transaction volume, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- User- Friendly Experience: Mobile apps and websites created for m-commerce are frequently optimised for smaller screens, resulting in a smoother, more user friendly buying experience than traditional e-commerce platforms.
Factors Affecting M- Commerce
1. Technology Advancements:
– Smartphone Adoption: The proliferation of smartphones and high-speed internet connectivity is essential for increasing m-commerce activity.
– Mobile Apps and Websites: User-friendly, secure, and responsive mobile applications and websites enhance the shopping experience.
2. Payment Solutions:
– Mobile Payment Systems: Availability and acceptance of mobile payment options (like digital wallets and contactless payments) can influence consumer behaviour.
– Security Concerns: Perceived security risks associated with mobile transactions may deter users.
3. Consumer Behaviour:
– Convenience: The need for convenience drives consumers to use mobile devices for shopping.
– Shopping Preferences: Trends in consumer behaviour, such as preference for online shopping over traditional retail, play a crucial role.
4. Marketing Strategies:
– Personalization: Tailored marketing and personalized offers can enhance user engagement and sales.
– Social Media Influence: Social media platforms are becoming vital channels for m-commerce, impacting consumer purchasing decisions.
5. Internet Connectivity:
– Network Speed and Availability: High-speed mobile internet and widespread availability significantly boost m-commerce activities.
– 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G networks promises faster internet speeds, improving the shopping experience.
6. User Experience:
– Interface Design: A well-designed user interface and seamless navigation on mobile platforms can enhance the shopping experience.
– Customer Support: Effective customer service and support can influence customer satisfaction and retention.
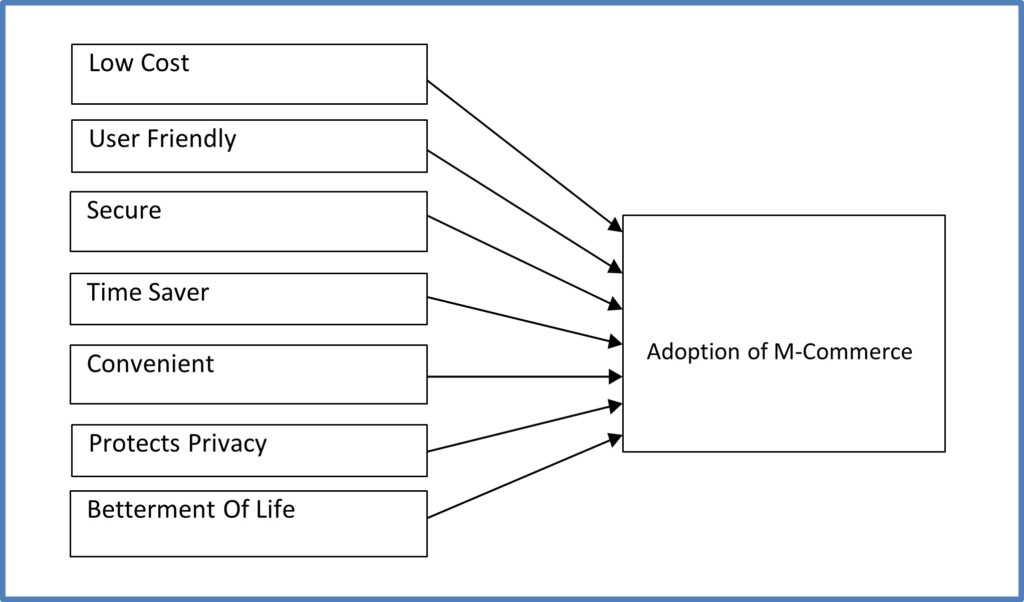
Important variables of adoption of M- Commerce
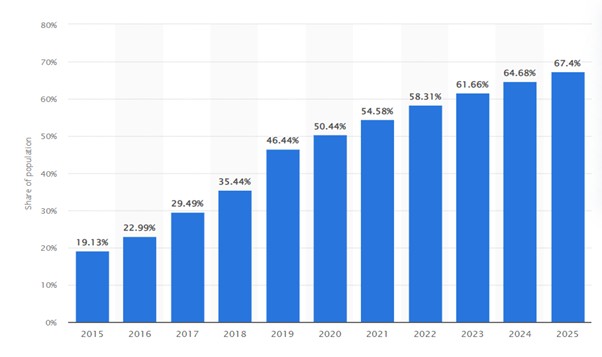
Growth of M- Commerce In India
Challenges of M- Commerce
- Digital Literacy: A significant portion of the population lacks basic digital literacy, which hampers their ability to engage in m-commerce. Understanding how to navigate apps and websites can be a barrier, particularly in rural areas.
- Infrastructure Issues: While urban areas have better connectivity, many rural regions face issues like poor internet coverage and slow data speeds. This can lead to a subpar user experience and deter consumers from using mobile commerce platforms.
- Security Concerns: Issues related to data privacy and security are significant barriers for users. Concerns about online fraud, data breaches, and secure payment methods can discourage potential customers from engaging in m-commerce.
- Payment Gateways: Inadequate or unreliable payment gateway solutions can lead to transaction failures, which frustrate users and lead to loss of sales. Additionally, many people may not have access to credit or debit cards, complicating payment processes.
- Competition and Market Saturation: The m-commerce space is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for consumer attention. This saturation can lead to a struggle for differentiation and profitability among companies.
- Consumer Trust: Building trust in mobile platforms is crucial. Many consumers may still prefer traditional shopping methods over mobile platforms due to uncertainty about product quality, return policies, and customer service.
- Logistics and Delivery Challenges: Inefficiencies in logistics and supply chain management can hinder timely delivery of products, especially in remote areas. This can impact customer satisfaction and overall trust in m-commerce.
- Regional Language Barriers: India is a linguistically diverse country, and most m-commerce platforms primarily operate in English. This can alienate non-English speaking users, limiting the market reach.
- Regulatory and Compliance Issues: Navigating the regulatory landscape can be complex for m-commerce businesses. Complying with government regulations and policies, including GST registration and consumer protection laws, can be challenging.
- User Experience and App Performance: Poor app performance, including slow loading times or complicated navigation, can drive users away. Ensuring a seamless and intuitive user experience is crucial but can be difficult to achieve.
Conclusion
This study sought to identify the factors influencing the adoption of M-commerce. Confirmatory factor analysis was done to verify the factors. Seven factors were identified, and all are important. These considerations include perceived utility, perceived ease of use, trust, subjective norms, perceived value added, privacy, and security. The perceived ease of use was found to have no significant relationship with mobile users’ behaviour intentions toward m-commerce. This study was written to provide a thorough understanding of the major aspects that influence consumer behaviour when adopting M-commerce in India. If consumers have improved internet access and a trustworthy interface, they are more likely to participate in mobile purchasing and, as a result, adopt m-commerce. However, it still confronts a number of obstacles that impede its expansion and adoption. The findings show that perceived credibility risk, defined as security risk and privacy risk, is significantly connected with behavioural intention in a negative relationship, implying that security and privacy concerns are crucial in discouraging customers from utilizing mobile commerce. Businesses that examine these aspects can design strategies to better engage with customers, improve the mobile shopping experience, and compete in the m-commerce market.
References
- Sugabrodhayini, M. (2022). “A study on consumer perception on the impact of M-Commerce in Chengalpattu. International Journal of Research Publications and Reviews. Vol. 3 Issue 7.
- CHEN, Zhi. CHEN, XI, (2011). “A Survey Study on consumer perception of mobile commerce applications.” Procedia Environmental Sciences 11. 118-124.
- Shrivas, K. Tiwari, A. (2017). “A study of M-Commerce in India.” Indian Journal of Applied research. Vol. 7. Issue 3.
- Baker, A. Abbas, N. (2019). “M-Commerce Potentials and Challenges.” International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering. Vol. 8.
- Bhople, M. (2018). “Study of M-Commerce applications users in India with different perspectives.” International Journal of Advanced Science and Research. Vol. 3. Issue 1.
- Kanchana, K. (2018). “A study on M-Commerce and Mobile Apps” International Journal of Research. Vol. 5. Issue 4.
- Jahanashahi, AA. (2011). “Mobile Commerce Beyond Electronic Commerce issue and Challenges.” Asian Journal of Business and Management Science. 1(2).
- Thakwani, P. (2014). “The Awareness of M-Commerce amongst customers Today.” International Journal of Scientific & Engineering research, Volume 5, issue 12 December (2014) ISSN 2229-5518.
- Nuzuk, O. Gitan. (2014). “Analysis of Determinants of M-Commerce Adoption by online consumers.” International Journal of Business Humanities and technology. Vol. 4.
- Jain, G. (2018). “M-Commerce in India: A step Towards Technology.” (JETIR) Vol. 5. Issue 3.
- Wasiq, M. Ahmad, N. (2016). “Future of M-Commerce Services in India.” Internal Journal of Marketing & Financial Management 2348-3954
About Author
Ms. Ranju is a Research Scholar in the Department of Commerce at NIILM University and pursuing her Ph.D. under the supervision of Dr Bharat Bhushan. She has written and presented many research papers at various National and International Conferences and Seminars.
Impact Statement
The rapid proliferation of smartphones, affordable internet access, and digital payment systems has transformed India into one of the fastest-growing mobile commerce (m-commerce) markets globally. This analysis of factors affecting mobile commerce in India provides critical insights into the drivers, challenges, and opportunities shaping the industry. The findings of this study have significant implications for businesses, policymakers, and consumers, contributing to the sustainable growth of the digital economy in India.

